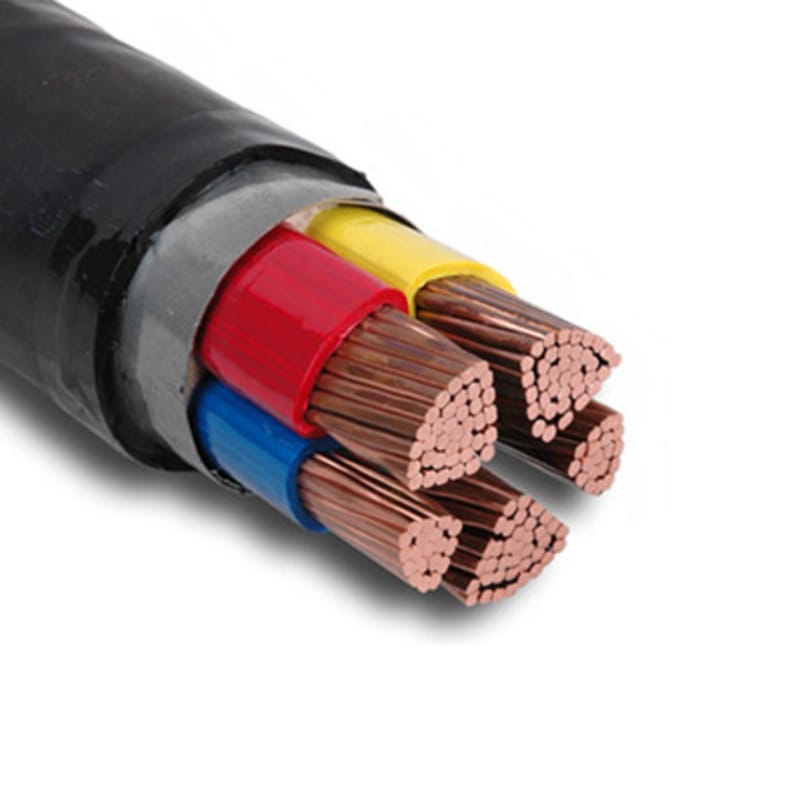
0,6/1 kV CU/XLPE/PVC-Stahlband-Panzerkabel
Anwendung
Xlpe-isoliertes, mit PVC ummanteltes, mit Stahlband gepanzertes Kabel besteht aus reinem Kupferleiter, XLPE-Isolierung, Stahlbandpanzerung und flammhemmendem PVC-Mantel.Mehradrige Industriekabel sind für eine Nennspannung von 0,6/1 kV geeignet und können einer bestimmten mechanischen Schwerkraft standhalten. Sie können für Kraftwerke, U-Bahnen, Tunnel, Hochhäuser, große Industrie- und Bergbauunternehmen, Ölfelder, Kohlebergwerke und andere verwendet werden Orte mit intensiv verteilten Elektrokabeln.
Konstruktion
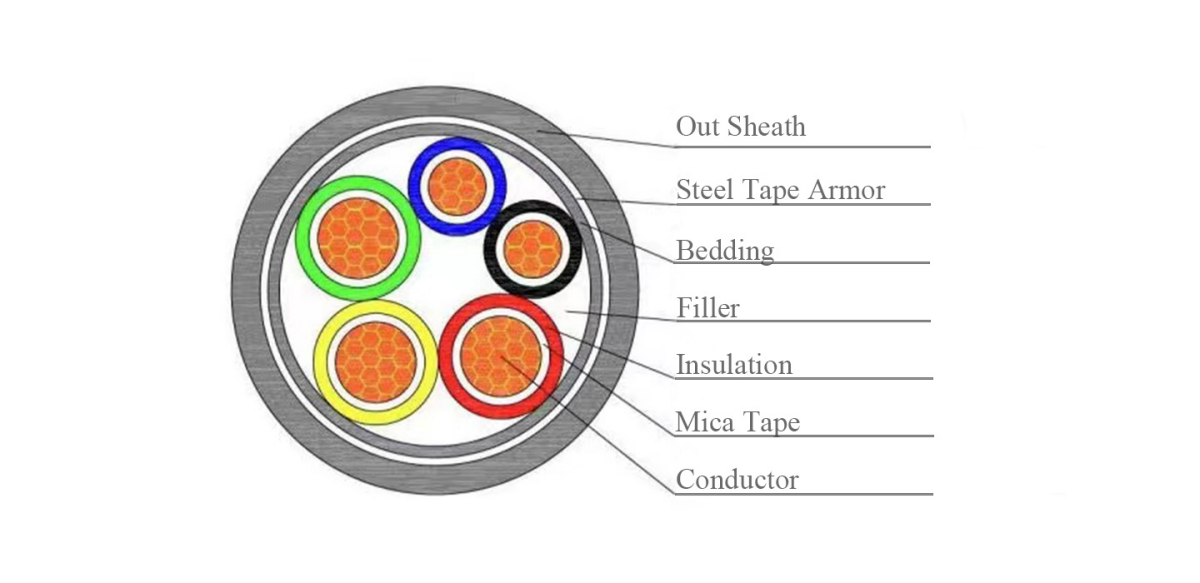
Eigenschaften
Nennspannung: 0,6 / 1 kV
Maximale Leitertemperatur: unter normalen (90℃), Notfall- (130℃) oder Kurzschlussbedingungen nicht länger als 5 s (250℃).
Mindest.Umgebungstemparatur.0℃, nach der Installation und nur, wenn das Kabel in einer festen Position ist
Mindest.Biegeradius: 12 x Kabel-Außendurchmesser für mehradrige Kabel
Standards
IEC 60502-1, GB/T 12706.1
Parameter
| 2 KernStahlband-Panzerkabel | ||||||||||
| Nom.Querschnitt des Leiters | Isolationsstärke | Dicke der inneren Abdeckung | Dicke des Stahlbandes | Manteldicke | Ca.OD | Geschätztes Gewicht | Max.Gleichstromwiderstand des Leiters (20 °C) | Prüfspannung AC | Aktuelle Bewertung | |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | Ω/km | kV/5min | In Luft(A) | Im Boden(A) |
| 2x4 | 0,7 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 15 | 433 | 4.61 | 3.5 | 34 | 45 |
| 2×6 | 0,7 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 16 | 500 | 3.08 | 3.5 | 43 | 57 |
| 2×10 | 0,7 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 19 | 673 | 1,83 | 3.5 | 60 | 77 |
| 2×16 | 0,7 | 1.4 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 21 | 857 | 1.15 | 3.5 | 83 | 105 |
| 2×25 | 0,9 | 1.4 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 24 | 1173 | 0,727 | 3.5 | 105 | 125 |
| 2×35 | 0,9 | 1.6 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 25 | 1449 | 0,524 | 3.5 | 125 | 155 |
| 2×50 | 1 | 1.6 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 26 | 1877 | 0,387 | 3.5 | 160 | 185 |
| 2×70 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 2x0,2 | 1.8 | 27 | 2454 | 0,268 | 3.5 | 200 | 225 |
| 2×95 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 2x0,2 | 1.9 | 30 | 2483 | 0,193 | 3.5 | 245 | 270 |
| 2×120 | 1.2 | 2 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 33 | 4213 | 0,153 | 3.5 | 285 | 310 |
| 2×150 | 1.4 | 2 | 2x0,5 | 2.2 | 38 | 5087 | 0,124 | 3.5 | 325 | 345 |
| 3-adriges, mit Stahlband gepanzertes Kabel | ||||||||||
| Nom.Querschnitt des Leiters | Isolationsstärke | Dicke der inneren Abdeckung | Dicke des Stahlbandes | Manteldicke | Ca.OD | Geschätztes Gewicht | Max.Gleichstromwiderstand des Leiters (20 °C) | Prüfspannung AC | Aktuelle Bewertung | |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | Ω/km | kV/5min | In Luft(A) | Im Boden(A) |
| 3x1,5 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 13 | 273 | 12.1 | 3.5 | 20 | 27 |
| 3x2,5 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 14 | 321 | 7.41 | 3.5 | 26 | 35 |
| 3×4 | 0,7 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 15 | 390 | 4.61 | 3.5 | 34 | 45 |
| 3×6 | 0,7 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 16 | 471 | 3.08 | 3.5 | 43 | 57 |
| 3×10 | 0,7 | 1.4 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 18 | 622 | 1,83 | 3.5 | 60 | 77 |
| 3×16 | 0,7 | 1.4 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 22 | 1005 | 1.15 | 3.5 | 83 | 105 |
| 3×25 | 0,9 | 1.6 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 25 | 1371 | 0,727 | 3.5 | 105 | 125 |
| 3×35 | 0,9 | 1.6 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 27 | 1724 | 0,524 | 3.5 | 125 | 155 |
| 3×50 | 1 | 1.8 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 30 | 2247 | 0,387 | 3.5 | 160 | 185 |
| 3×70 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 2x0,2 | 2.5 | 35 | 3023 | 0,268 | 3.5 | 200 | 225 |
| 3×95 | 1.1 | 2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 39 | 3825 | 0,193 | 3.5 | 245 | 270 |
| 3×120 | 1.2 | 2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 42 | 4642 | 0,153 | 3.5 | 285 | 310 |
| 3×150 | 1.4 | 2 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 48 | 5767 | 0,124 | 3.5 | 325 | 345 |
| 3×185 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 51 | 6895 | 0,0991 | 3.5 | 375 | 390 |
| 3×240 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 56 | 8617 | 0,0754 | 3.5 | 440 | 450 |
| 3×300 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 59 | 10928 | 0,0601 | 3.5 | 505 | 515 |
| 3×400 | 2 | 2.2 | 2x0,5 | 3.2 | 61 | 13556 | 0,047 | 3.5 | 570 | 575 |
| 4-adriges, mit Stahlband gepanzertes Kabel | ||||||||||
| Nom.Querschnitt des Leiters | Isolationsstärke | Dicke der inneren Abdeckung | Dicke des Stahlbandes | Manteldicke | Ca.OD | Geschätztes Gewicht | Max.Gleichstromwiderstand des Leiters (20 °C) | Prüfspannung AC | Aktuelle Bewertung | |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | Ω/km | kV/5min | In Luft(A) | Im Boden(A) |
| 4×4 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 16 | 454 | 4.61 | 3.5 | 34 | 45 |
| 4×6 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 17 | 557 | 3.08 | 3.5 | 43 | 57 |
| 4×10 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 20 | 791 | 1,83 | 3.5 | 60 | 77 |
| 4×16 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 23 | 1210 | 1.15 | 3.5 | 83 | 105 |
| 4×25 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 27 | 1672 | 0,727 | 3.5 | 105 | 125 |
| 4×35 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 29 | 2127 | 0,524 | 3.5 | 125 | 155 |
| 4×50 | 1 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 33 | 2802 | 0,387 | 3.5 | 160 | 185 |
| 4×70 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 2.5 | 38 | 3785 | 0,268 | 3.5 | 200 | 225 |
| 4×95 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 42 | 4829 | 0,193 | 3.5 | 245 | 270 |
| 4×120 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 47 | 6033 | 0,153 | 3.5 | 285 | 310 |
| 4×150 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 52 | 7356 | 0,124 | 3.5 | 325 | 345 |
| 4×185 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 56 | 8806 | 0,0991 | 3.5 | 375 | 390 |
| 4×240 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 62 | 11182 | 0,0754 | 3.5 | 440 | 450 |
| 4×300 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 2x0,5 | 3.1 | 64 | 14176 | 0,0601 | 3.5 | 505 | 515 |
| 4×400 | 2 | 1.7 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 69 | 17815 | 0,047 | 3.5 | 570 | 575 |
| 5-adriges, mit Stahlband gepanzertes Kabel | ||||||||||
| Nom.Querschnitt des Leiters | Isolationsstärke | Dicke der inneren Abdeckung | Dicke des Stahlbandes | Manteldicke | Ca.OD | Geschätztes Gewicht | Max.Gleichstromwiderstand des Leiters (20 °C) | Prüfspannung AC | Aktuelle Bewertung | |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | Ω/km | kV/5min | In Luft(A) | Im Boden(A) |
| 5×4 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 17.1 | 588 | 4.61 | 3.5 | 34 | 45 |
| 5×6 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 19.4 | 720 | 3.08 | 3.5 | 43 | 57 |
| 5×10 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 22.9 | 1014 | 1,83 | 3.5 | 60 | 77 |
| 5×16 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 25.8 | 1392 | 1.15 | 3.5 | 83 | 105 |
| 5×25 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 30.5 | 2002 | 0,727 | 3.5 | 105 | 125 |
| 5×35 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 33.7 | 2581 | 0,524 | 3.5 | 125 | 155 |
| 5×50 | 1 | 1 | 2x0,5 | 2 | 38.6 | 3722 | 0,387 | 3.5 | 160 | 185 |
| 5×70 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 43.4 | 4897 | 0,268 | 3.5 | 200 | 225 |
| 5×95 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 48.6 | 6338 | 0,193 | 3.5 | 245 | 270 |
| 5×120 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 54.4 | 7851 | 0,153 | 3.5 | 285 | 310 |
| 5×150 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 60.1 | 9661 | 0,124 | 3.5 | 325 | 345 |
| 5×185 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 66,7 | 11770 | 0,0991 | 3.5 | 375 | 390 |
| 5×240 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 74,7 | 14900 | 0,0754 | 3.5 | 440 | 450 |
| 5×300 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 2x0,5 | 3.1 | 83,2 | 18000 | 0,0601 | 3.5 | 505 | 515 |
| 3+1-adriges Stahlband-Panzerkabel | ||||||||||
| Nom.Querschnitt des Leiters | Isolationsstärke | Dicke der inneren Abdeckung | Dicke des Stahlbandes | Manteldicke | Ca.OD | Geschätztes Gewicht | Max.Gleichstromwiderstand des Leiters (20 °C) | Prüfspannung AC | Aktuelle Bewertung | |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | Ω/km | kV/5min | In Luft(A) | Im Boden(A) |
| 3×4 + 1×2,5 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 16 | 443 | 4.61 | 3.5 | 34 | 45 |
| 3×6 + 1×4 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 17 | 531 | 3.08 | 3.5 | 43 | 57 |
| 3×10 + 1×6 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 20 | 741 | 1,83 | 3.5 | 60 | 77 |
| 3×16 + 1×10 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 23 | 1135 | 1.15 | 3.5 | 83 | 105 |
| 3×25 + 1×16 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 26 | 1556 | 0,727 | 3.5 | 105 | 125 |
| 3×35 + 1×16 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 28 | 1896 | 0,524 | 3.5 | 125 | 155 |
| 3×50 + 1×25 | 1 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 31 | 2518 | 0,387 | 3.5 | 160 | 185 |
| 3×70 + 1×35 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 2.5 | 36 | 3293 | 0,268 | 3.5 | 200 | 225 |
| 3×95 + 1×50 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 40 | 4349 | 0,193 | 3.5 | 245 | 270 |
| 3×120 + 1×70 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 44 | 5365 | 0,153 | 3.5 | 285 | 310 |
| 3×150 + 1×70 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 49 | 6468 | 0,124 | 3.5 | 325 | 345 |
| 3×185 + 1×95 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 52 | 7854 | 0,0991 | 3.5 | 375 | 390 |
| 3×240 + 1×120 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 68 | 9814 | 0,0754 | 3.5 | 440 | 450 |
| 3×300 + 1×150 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 71 | 12781 | 0,0601 | 3.5 | 505 | 515 |
| 3×400 + 1×240 | 2 | 1.7 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 76 | 16359 | 0,047 | 3.5 | 570 | 575 |
| 3+2-adriges Stahlband-Panzerkabel | ||||||||||
| Nom.Querschnitt des Leiters | Isolationsstärke | Dicke der inneren Abdeckung | Dicke des Stahlbandes | Manteldicke | Ca.OD | Geschätztes Gewicht | Max.Gleichstromwiderstand des Leiters (20 °C) | Prüfspannung AC | Aktuelle Bewertung | |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | Ω/km | kV/5min | In Luft(A) | Im Boden(A) |
| 3×4 + 2×2,5 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 17.5 | 855 | 4.61 | 3.5 | 34 | 45 |
| 3×6 + 2×4 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 18.9 | 1009 | 3.08 | 3.5 | 43 | 57 |
| 3×10 + 2×6 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 21.6 | 1461 | 1,83 | 3.5 | 60 | 77 |
| 3×16 + 2×10 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 24.6 | 1877 | 1.15 | 3.5 | 83 | 105 |
| 3×25 + 2×16 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 28.7 | 2583 | 0,727 | 3.5 | 105 | 125 |
| 3×35 + 2×16 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 30.7 | 3001 | 0,524 | 3.5 | 125 | 155 |
| 3×50 + 2×35 | 1 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 36.2 | 4392 | 0,387 | 3.5 | 160 | 185 |
| 3×70 + 2×35 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,2 | 2.5 | 40.3 | 5519 | 0,268 | 3.5 | 200 | 225 |
| 3×95 + 2×50 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 44.9 | 7543 | 0,193 | 3.5 | 245 | 270 |
| 3×120 + 2×70 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 50.3 | 9203 | 0,153 | 3.5 | 285 | 310 |
| 3×150 + 2×70 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 54 | 10485 | 0,124 | 3.5 | 325 | 345 |
| 3×185 + 2×95 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 60.2 | 13945 | 0,0991 | 3.5 | 375 | 390 |
| 3×240 + 2×120 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 67.2 | 15643 | 0,0754 | 3.5 | 440 | 450 |
| 3×300 + 2×150 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 75,2 | 18204 | 0,0601 | 3.5 | 505 | 515 |
| 4+1-adriges, mit Stahlband gepanzertes Kabel | ||||||||||
| Nom.Querschnitt des Leiters | Isolationsstärke | Dicke der inneren Abdeckung | Dicke des Stahlbandes | Manteldicke | Ca.OD | Geschätztes Gewicht | Max.Gleichstromwiderstand des Leiters (20 °C) | Prüfspannung AC | Aktuelle Bewertung | |
| mm2 | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/km | Ω/km | kV/5min | In Luft(A) | Im Boden(A) |
| 4×4 + 1×2,5 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 18.4 | 565 | 4.61 | 3.5 | 34 | 45 |
| 4×6 + 1×4 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 1.5 | 19.8 | 692 | 3.08 | 3.5 | 43 | 57 |
| 4×10 + 1×6 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 22.8 | 953 | 1,83 | 3.5 | 60 | 77 |
| 4×16 + 1×10 | 0,7 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 25.8 | 1318 | 1.15 | 3.5 | 83 | 105 |
| 4×25 + 1×16 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 30.4 | 1877 | 0,727 | 3.5 | 105 | 125 |
| 4×35 + 1×16 | 0,9 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 34.1 | 2324 | 0,524 | 3.5 | 125 | 155 |
| 4×50 + 1×25 | 1 | 1 | 2x0,2 | 2 | 38.7 | 3415 | 0,387 | 3.5 | 160 | 185 |
| 4×70 + 1×35 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 44.2 | 4432 | 0,268 | 3.5 | 200 | 225 |
| 4×95 + 1×50 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 49,8 | 5747 | 0,193 | 3.5 | 245 | 270 |
| 4×120 + 1×70 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 2x0,5 | 2.5 | 55.4 | 7112 | 0,153 | 3.5 | 285 | 310 |
| 4×150 + 1×70 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 60.1 | 8556 | 0,124 | 3.5 | 325 | 345 |
| 4×185 + 1×95 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 2x0,5 | 3 | 66,9 | 10510 | 0,0991 | 3.5 | 375 | 390 |
| 4×240 + 1×120 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 74,8 | 13232 | 0,0754 | 3.5 | 440 | 450 |
| 4×300 + 1×150 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 2x0,5 | 3.5 | 78,4 | 16452 | 0,0601 | 3.5 | 505 | 515 |

FAQ
F: Können wir unser Logo oder unseren Firmennamen auf Ihre Produkte oder die Verpackung drucken lassen?
A: Der OEM- und ODM-Auftrag ist uns herzlich willkommen und wir verfügen über umfassende Erfahrung mit OEM-Projekten.Darüber hinaus gibt Ihnen unser Forschungs- und Entwicklungsteam professionelle Vorschläge.
F: Wie schneidet Ihr Unternehmen bei der Qualitätskontrolle ab?
A: 1) Für alle Rohstoffe haben wir die hohe Qualität ausgewählt.
2) Professionelle und geschickte Mitarbeiter kümmern sich bei der Abwicklung der Produktion um jedes Detail.
3) Abteilung für Qualitätskontrolle, die speziell für die Qualitätsprüfung in jedem Prozess verantwortlich ist.
F: Wie kann ich ein Muster erhalten, um Ihre Qualität zu testen?
A: Wir können Ihnen kostenlose Muster für Ihre Tests und Überprüfungen zur Verfügung stellen. Sie müssen lediglich die Frachtkosten tragen.














